The urgency to fill store shelves left empty by supply-chain bottlenecks caused by the pandemic have increased food manufacturers’ willingness to explore new automation options made possible by an explosion of data in food production.
Take commercial bakeries, for example. Today’s bakers produce more than baked goods – they bake a lot of data too. The average industrial bakery produces upwards of 5 petabytes of data per day. That’s the equivalent of 39,063 128GB iPhone 13 Pros every single day! A strong incentive for automation through Artificial Intelligence (AI).
A recent Honeywell Report found that 59% of Food & Bev businesses want to invest in automation as a result of the pandemic.
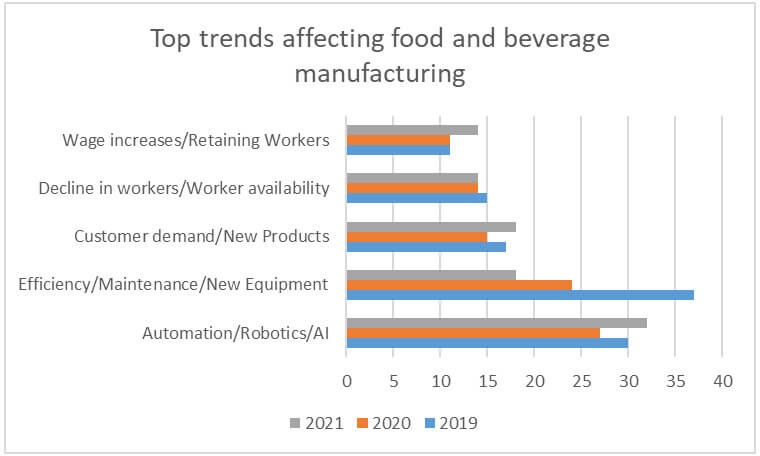
Furthermore, according to Food Engineering’s annual State of Food Manufacturing Survey, “automation/robotics/AI” was the number one trend expected to shape food manufacturing for the next five years [Figure 2].
But as food factories get smarter, we can expect the emergence of yet another bottleneck—a shortage of data scientists needed to develop AI solutions that will optimize our food production processes.
There is also the perception by many food manufacturers that AI is too expensive, too complex, and too inaccessible except for the biggest players in the industry.
Yet every food manufacturer can leverage their own data to minimize the impact of supply-chain disruptions by deploying intuitive AI solutions using No-Code visual programming platforms. Food manufacturers can optimize their supply chains using the following 3 proven AI solutions without the need for advanced programming skills:
- No-Code AI to Optimize Demand
- No-Code AI to Optimize Inventory
- No-Code AI to Optimize Traceability
But first, what is No-Code AI?
What is No-Code AI?
Simply put, no-code platforms make AI possible without the need for software programming. Through self-service analytics, we are able to connect, prepare, and model data without writing a single line of code, thereby opening the world of advanced analytics to those previously limited by a lack of experience in computer programming.
Why is this relevant to food manufacturers?
Well, previously food manufacturers had to rely on scarce data scientists to program complex algorithms. But now with the help of no-code platforms like KNIME (pronounced NAIM), skilled data analysts can visually program advanced solutions, thus accelerating the speed and effectiveness of AI for supply chain management.
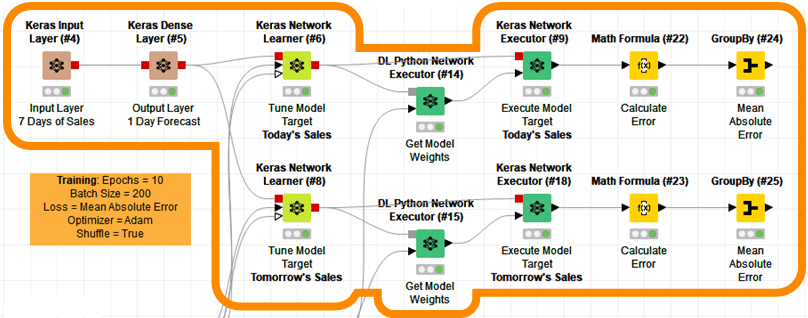
For example, Figure 3 shows a visually programed Deep Learning model in KNIME. All built using a drag-and-drop interface. No code required.
1. No-Code AI to Optimize Demand
The first AI solution that food manufacturers can use to optimize their supply chains is AI for demand forecasting.
Demand forecasting is the starting point for most supply-chain processes in food manufacturing, like raw material planning, procurement, inbound logistics, and production planning. It is therefore the key driver for all supply-chain related decisions.
With prices for production staples like flour and eggs skyrocketing 20% – 70% from a year ago, food manufacturers such as industrial bakers have little wiggle room when sourcing raw materials. Many are being forced to meet higher ingredient costs by reformulating their products with alternative ingredients.
Demand Forecasting AI for food are designed to learn from past historical product performance in order to predict future demand.
AI for demand forecasting is therefore the perfect strategic analytics tool food manufacturers can use to optimally allocate scarce resources and anticipate purchasing efforts with enough lead time to soften potential blows from slow supply chains.

AI’s potential in optimizing supply chains in food manufacturing is enormous. In fact, McKinsey Digital recently estimated a $1.2T-$2T total impact by AI in supply chain management and manufacturing through improved logistics and inventory costs alone.
What began as a simplified model of a brain neuron, Frank Rosenblatt’s Perceptron has evolved into advanced architectures of the cerebral cortex built entirely in software that learn by doing much as humans do [Figure 4].
Now, thanks to No-Code platforms like KNIME, the world of AI is open to everyone curious enough to explore its possibilities.
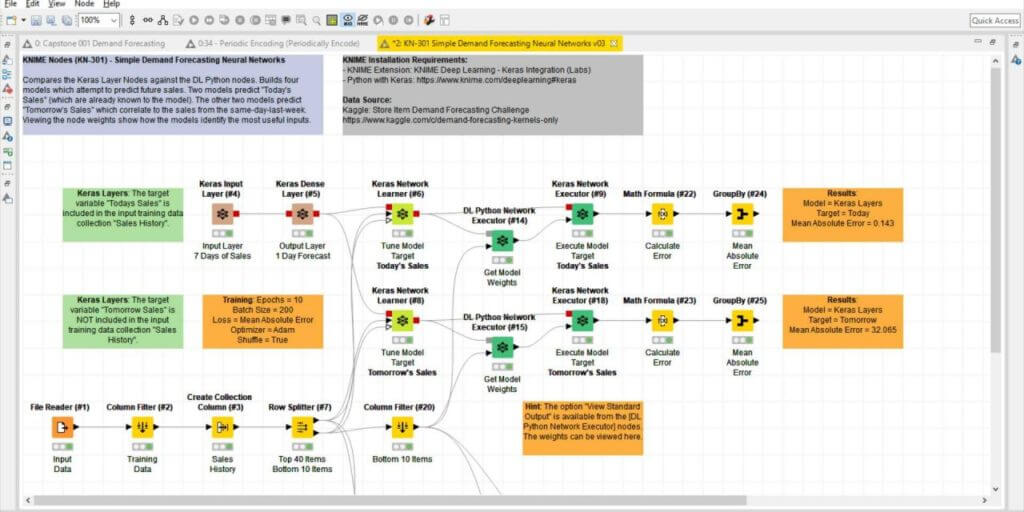
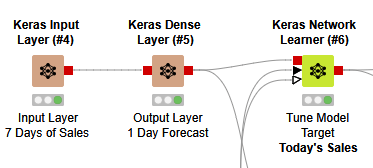
A simple example of a demand forecasting neural network is show in Figure 5. It shows how easy it is to visually program AI applications using a drag-and-drop interface to predict demand for food.
The KNIME workflow reads historical sales data to learn and predict future sales using a simple 3-layer Neural Network.
The workflow also compares how the native AI nodes in KNIME perform against a Deep Learning model written in the Python programming language. Yes, that is right, KNIME is code-free, but it’s also code-friendly, providing programmers and non-programmers alike a common platform with which to collaborate.
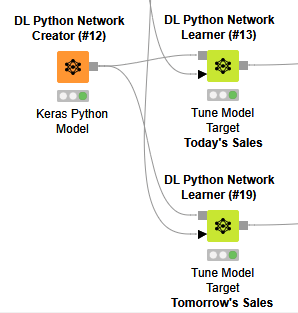
We’ve just seen how intuitive and visually elegant it is to develop advanced AI solutions for demand forecasting using No-Code platforms such as KNIME.
Another No-Code advantage is that it gives the option to quickly create a minimally viable product (MVP) or a proofs of concept (POC) in a fraction of the time it would take to develop them in code. Once the concept is proven, it can then be programmed using traditional methods or developed entirely in KNIME.
2. No-Code AI to Optimize Inventory
The second AI solution that food manufacturers can use to optimize their supply chains is AI for inventory forecasting.
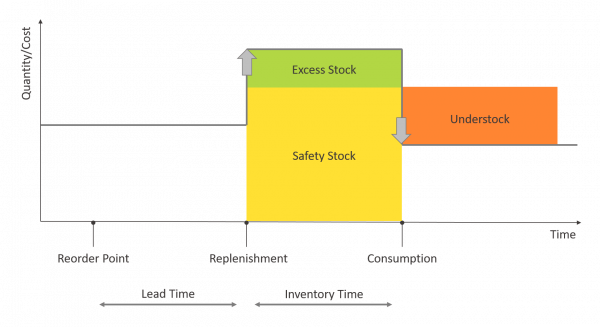
Inventory forecasting helps address supply chain disruptions by providing food manufacturers with optimal inventory levels to better plan their production and logistics. In combination with demand forecasting, manufacturers can efficiently purchase from suppliers based on accurate forecasts versus outdated procurement models.
Better forecasts also provide enough lead time to prevent stock-outs and thereby decreasing exposure to suppliers unable to meet demand while ensuring enough on-hand safety stock to fulfill orders.
AI for inventory optimization reads data from inventory management systems and analyzes past demand in order to predict optimal stock levels at any time. A well designed AI inventory forecasting solution will sync data across all systems (including ecommerce platforms) to ensure all orders and stock are accounted for.
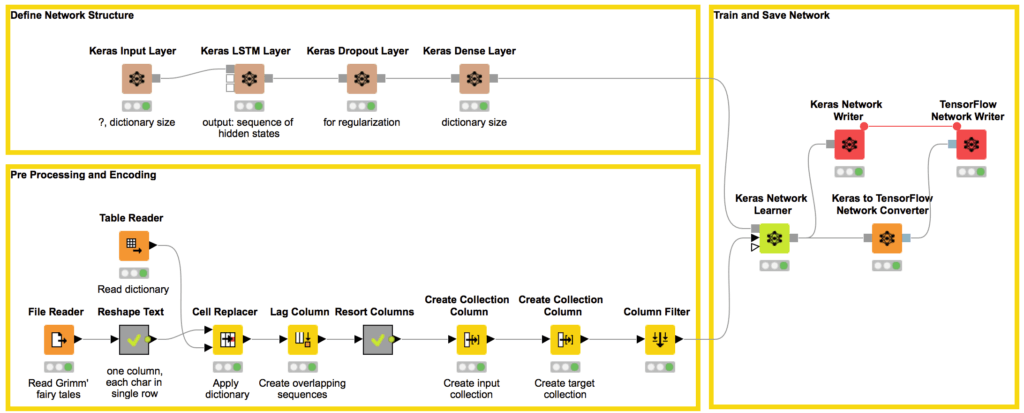
No-Code AI for Inventory Forecasting can be based on advanced time series methods such as Long-Short Term Memory Networks (LSTMs) or other Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) with sliding time windows to process sequential inventory data. In this way, the AI learns to spot patterns across time.
KNIME enables the codeless development of AI solutions for Inventory Forecasting. The workflow in Figure 8 shows how easy it is to ingest data and train a LSTM Network using the Keras nodes.
Another advantage of building AI for inventory forecasting in KNIME is it’s configurability and extensibility. For a food manufacturer to successfully navigate today’s complex supply chains, forecasting models need to be flexible enough to adapt to changing conditions. The model cannot be too rigid or it will be of no use.
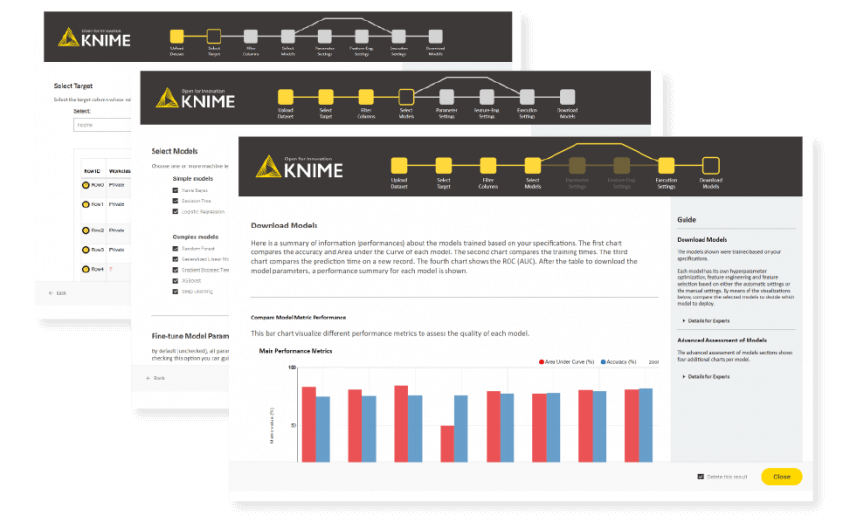
KNIME’s “Guided Analytics” feature allows AI solutions to be delivered and consumed via a web portal. Deployed as an app, end users can easily interact with and configure the model by changing parameters, datasets, and features to meet their specific requirements and finetune the forecast as conditions change (Figure 9).
3. No-Code AI to Optimize Traceability
The third AI solution that food manufacturers can use to optimize their supply chains is AI for traceability optimization.
Traceability enables food manufacturers to track the movement of products and ingredients through each step of the supply chain and manufacturing process. Traceability systems are crucial for the health and safety of the food supply.
In the case of foodborne illnesses or contamination, the linkages between food producers, processors, and distributors are maintained to enable faster removal of contaminated food. This helps reduce friction in the supply chain and enhances a food manufacturer’s agility when disruptions, such as food recalls, occur.
My company, Haystack Data Solutions, recently participated in The FDA New Era of Smarter Food Safety Low- or No-Cost Tech-Enabled Traceability Challenge to design a low-cost traceability solution for food manufacturers. We chose to build our solution in KNIME because of its extensive capabilities, but also because it is open-source (i.e. free).
Our solution was unique in its ability to combine all data sources and processing steps for a food manufacturer, while simultaneously visually documenting the logic used in the form of flowcharts that anyone can understand. This also makes it easy to run trace audits when a recall has occurred. You can see our FDA submission video below.
Our No-Code food traceability solution was born from real-world use cases of batch food manufacturers that wanted a fast, low-cost, reliable solution to automate previously time-consuming trace recalls.
From input lots to output packaging, most food manufacturers track their processing steps using a combination of spreadsheets and paper. It can take days or weeks for forensic analysis to manually trace a tainted food product this way.
- Track all inputs and outputs for complete visibility.
- Connect to all existing data sources (Databases, ERPs, MRPs, WMSs, etc.).
- Automatically flag food safety issues to initiate and complete an internal trace recall within minutes.
- Comply with all regulatory requirements.
- Do all this w/o writing a line of code or spending $.
Another example of a full end-to-end No-Code AI for food traceability is BfROpenLab’s FoodChain-Lab (Figure 10). Developed at the Federal Institute for Risk Assessment in Germany (BfR), FoodChain-Lab is a free KNIME package for full trace back and trace forward of suspicious food items along food supply chains during a foodborne disease outbreak.
It provides KNIME Nodes for GIS and Graph Visualization, Nonlinear Regression, and Network Mining for a complete traceability solution in KNIME (Figure 11).
Supply Chain AI is Accessible to all Food Manufacturers!
The pandemic has led to increased volatility in food manufacturing. Nowhere is this more evident than in today’s broken supply chains. Prices for raw ingredients are skyrocketing and orders arrive late or not at all.
But unprecedented times call for unprecedented measures. At no other time in history have food manufacturers had so much digital information at their fingertips. But, in order to make effective use of this data, manufacturers will need to redesign their supply-chain and digital processes. Investing in AI automation is crucial for future competitiveness, and the cost of not automating is simply too high in today’s landscape.
There is no better time to build the intelligent, resilient supply chains of tomorrow. Thanks to No-Code, Artificial Intelligence is now accessible to every food manufacturer who wishes to harness a new era of machine intelligence. By apply intuitive, drag-and-drop AI solutions for demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and food traceability, food manufacturers will be in a better position to weather supply chain disruptions when the next shock to the global food system occurs.
Are you ready to begin your No-Code AI journey?